Explore the five interventions to help you persuade your government officials why they should implement them.

Road environments designed to reduce vehicle speeds to 30 km/h (20 mph) or lower. This is achieved through 30 km/h (20 mph) posted speed limits, supported by speed enforcement, traffic calming measures, and pedestrian facilities to ensure the safety of pedestrians, cyclists, and motorcyclists.

Lowering legally-allowed maximum speed limits using speed limit signage to provide safe mobility for all road users. Lower speed limits are most effective when supported with traffic calming measures and/or enforcement to increase compliance with the legal limit.

Pedestrian facilities include footpaths—paths that are dedicated to pedestrians and physically separated from motorized traffic—and pedestrian crossings—road crossing points that give legal priority to pedestrians.

Traffic calming measures reduce speed of traffic in areas where pedestrians, cyclists, and motorcyclists are present, road infrastructure safety quality is poor, and/or vehicles enter a built-up area on a rural road.

A law mandating the correct use of helmets by motorcycle drivers and passengers of all ages while riding motorcycles. The law must also require the helmets to meet the safety standard (national or international), i.e., demonstrated to be effective in reducing head injuries for motorcycle riders. The law must be combined with enforcement that applies penalties for non-compliance and promotion that warns people about the law, enforcement, and penalties.
These five interventions have been prioritized because:
Advocating for one specific intervention can be more effective than a more general call for action. It makes budget needs more transparent and allows more concrete planning. It also makes it easier to monitor the implementation, and demonstrate results and build community buy-in and demand for the intervention (solution).
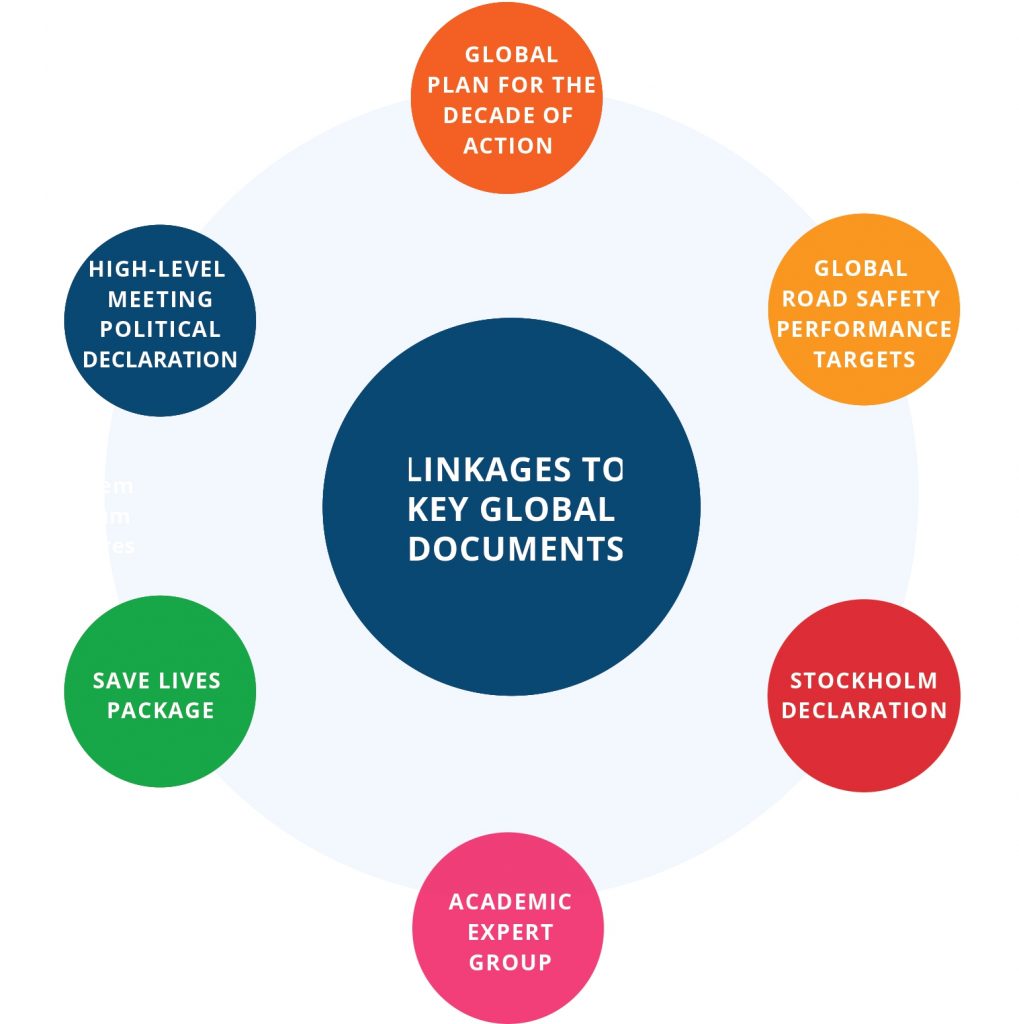
By implementing these five interventions, governments contribute to achieving recommendations and commitments in key global documents.